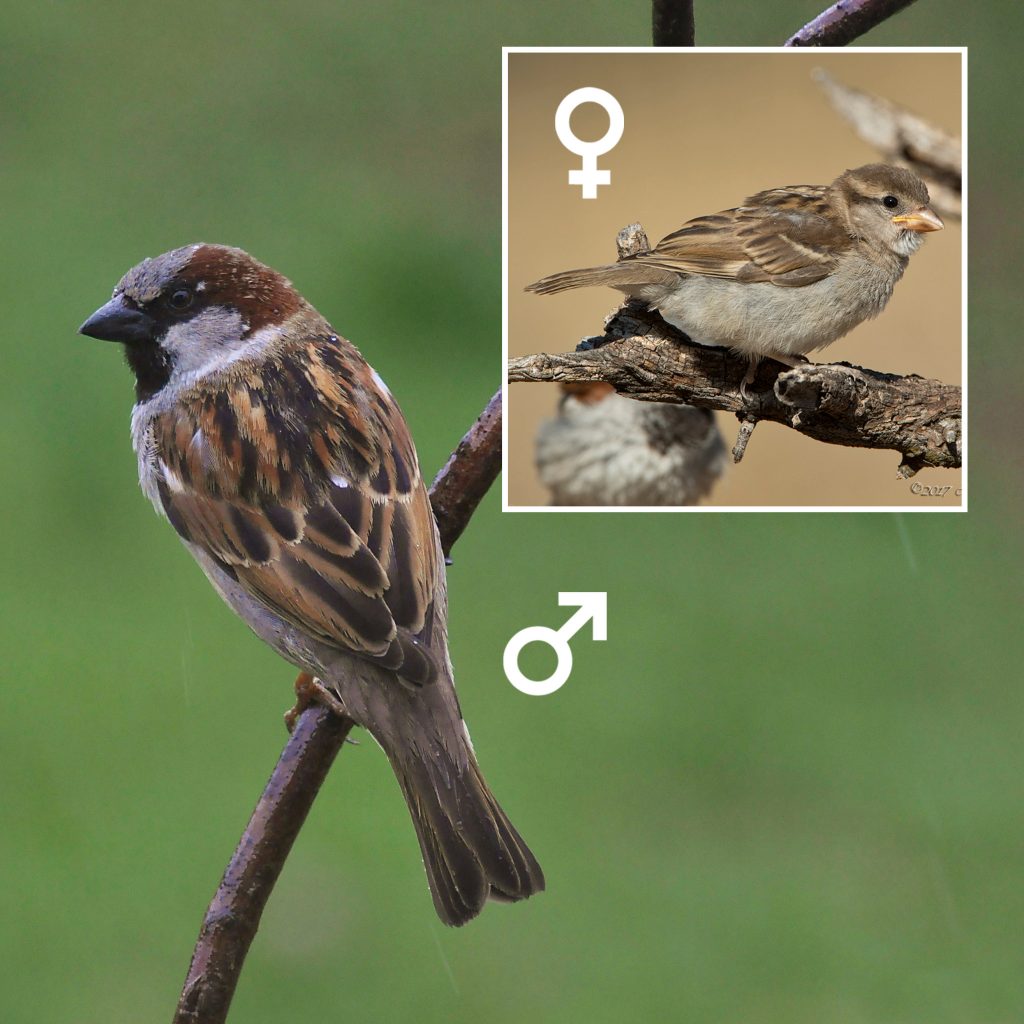
House Sparrow
Regional Species
You can find House Sparrows most places where there are houses (or other buildings), and few places where there aren’t. Along with two other introduced species, the European Starling and the Rock Pigeon, these are some of our most common birds. Their constant presence outside our doors makes them easy to overlook, and their tendency to displace native birds from nest boxes causes some people to resent them. But House Sparrows, with their capacity to live so intimately with us, are just beneficiaries of our own success.
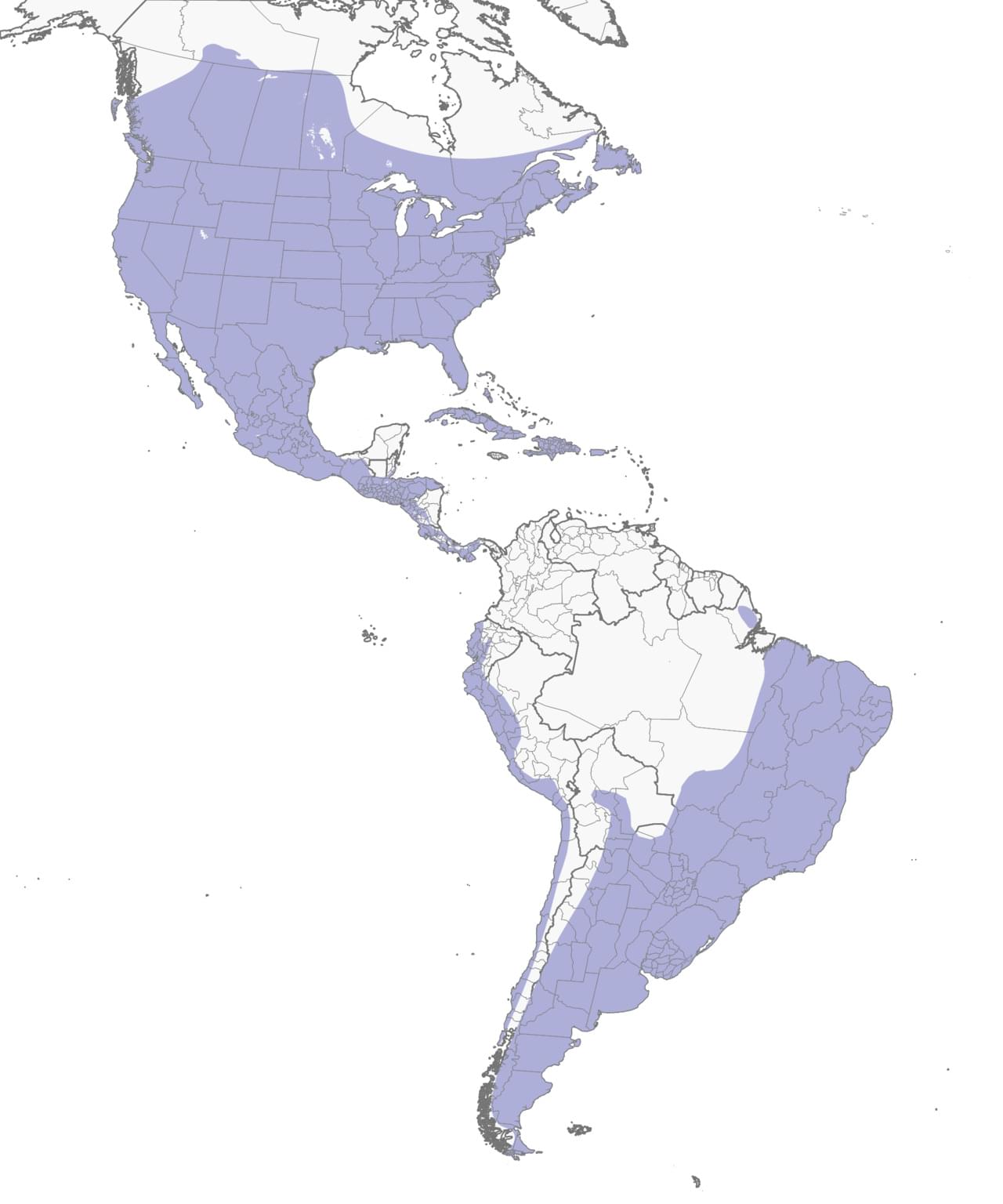
Range
Habitat
House Sparrows are closely associated with people and their buildings. Look for them in cities, towns, suburbs, and farms (particularly around livestock). You won’t find them in extensive woodlands, forests, or grasslands. In extreme environments such as deserts or the far north, House Sparrows survive only in the immediate vicinity of people.
Food
House Sparrows eat mostly grains and seeds, as well as livestock feed and, in cities, discarded food. Among the crops they eat are corn, oats, wheat, and sorghum. Wild foods include ragweed, crabgrass and other grasses, and buckwheat. House Sparrows readily eat birdseed including millet, milo, and sunflower seeds. Urban birds readily eat commercial bird seed. In summer, House Sparrows eat insects and feed them to their young. They catch insects in the air, by pouncing on them, or by following lawnmowers or visiting lights at dusk.
Behavior
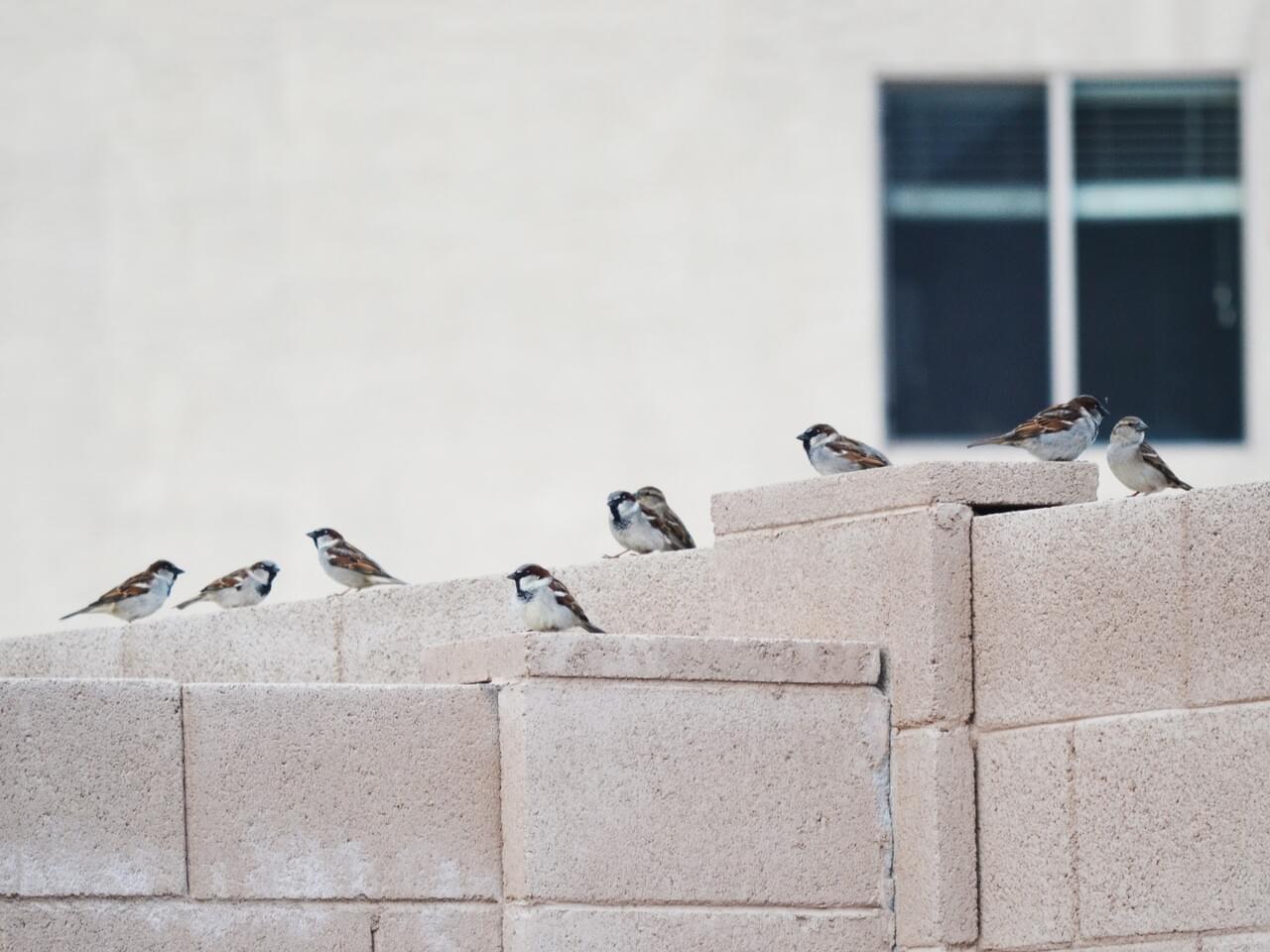
House Sparrows hop rather than walk on the ground. They are social, feeding in crowded flocks and squabbling over crumbs or seeds on the ground. House Sparrows are a common sight at bird feeders; you may also see them bathing in street-side puddles or dustbathing on open ground, ruffling their feathers and flicking water or dust over themselves with similar motions. From living in such close company, House Sparrows have developed many ways of indicating dominance and submission. Nervous birds flick their tails. Aggravated birds crouch with the body horizontal, shove their head forward and partially spread and roll forward their wings, and hold the tail erect. This can intensify to a display with wings lifted, crown and throat feathers standing on end, tail fanned, and beak open. Males with larger amounts of black on the throat tend to dominate over males with less black. When males display to a prospective mate, they fluff up their chest, hold their wings partially open, fan the tail, and hop stiffly in front of the female, turning sideways and sometimes bowing up and down. Sometimes, other males who spot such a display in progress will fly in and begin displaying as well. In flocks, males tend to dominate over females in fall and winter, but females assert themselves in spring and summer.
Nesting
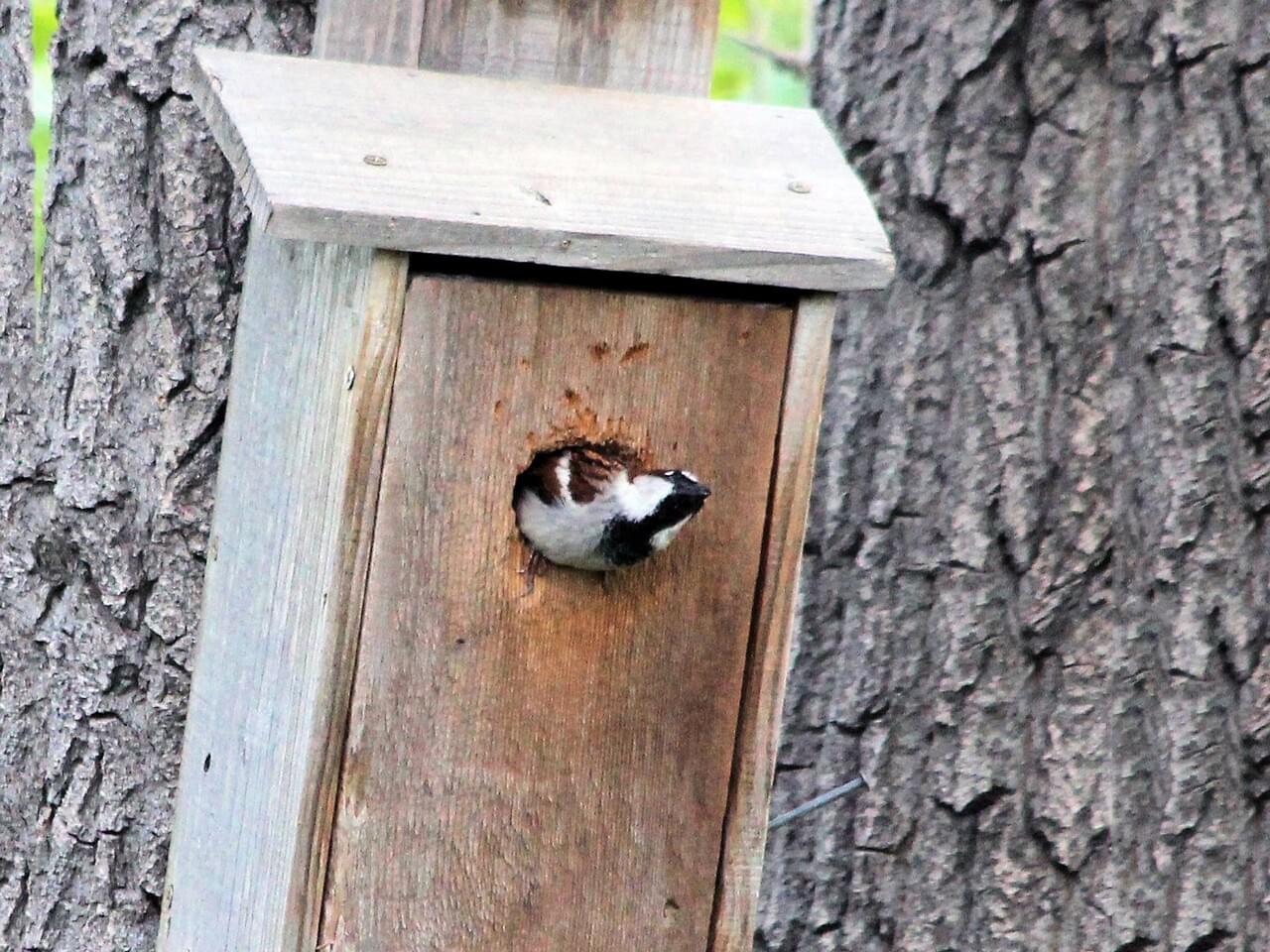
House Sparrow nests are made of coarse dried vegetation, often stuffed into the hole until it’s nearly filled. The birds then use finer material, including feathers, string, and paper, for the lining. House Sparrows sometimes build nests next to each other, and these neighboring nests can share walls. House Sparrows often reuse their nests.
Appearance
Typical Sound

© Brad Walker | Macaulay Library
Size & Shape
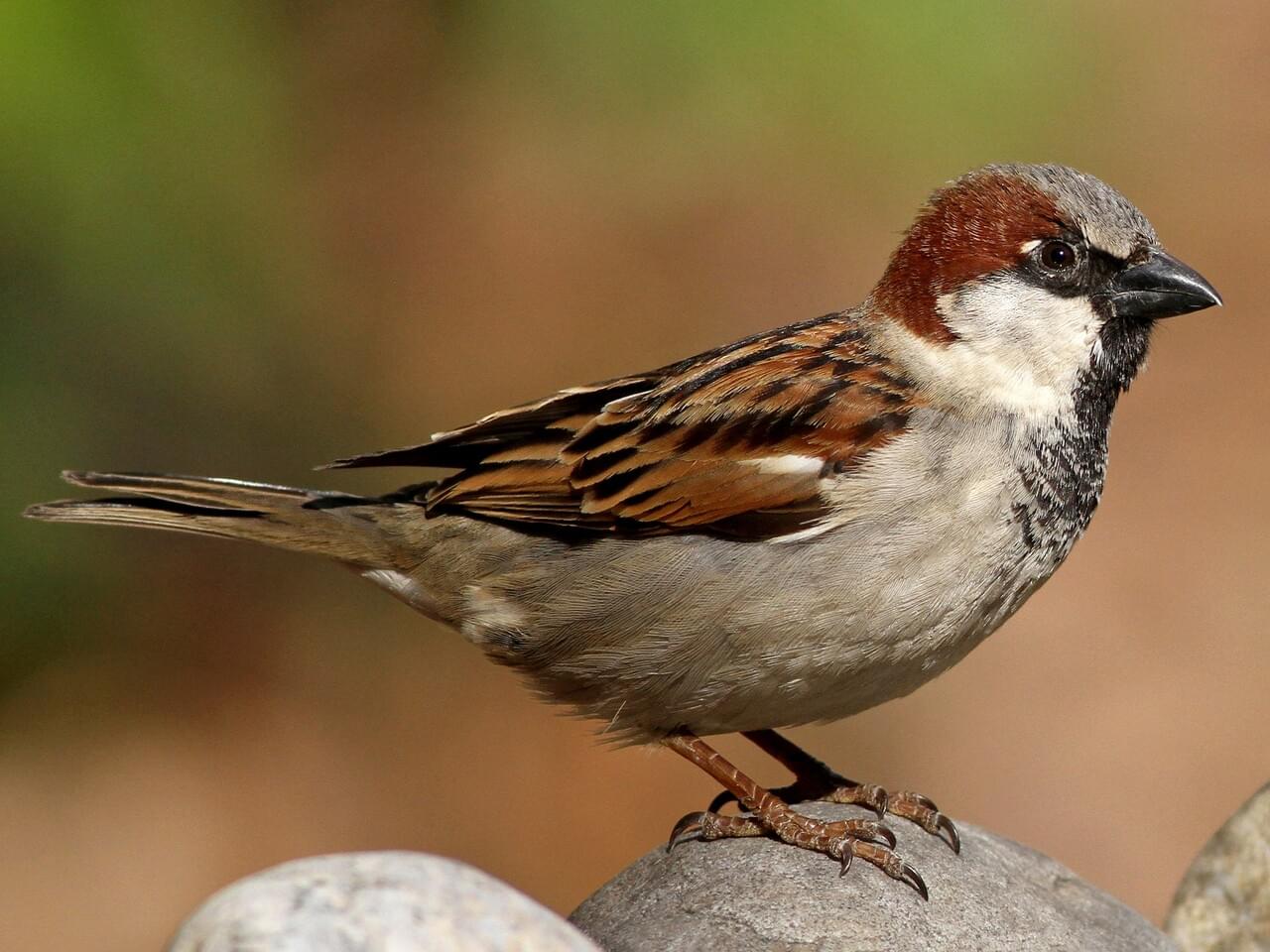
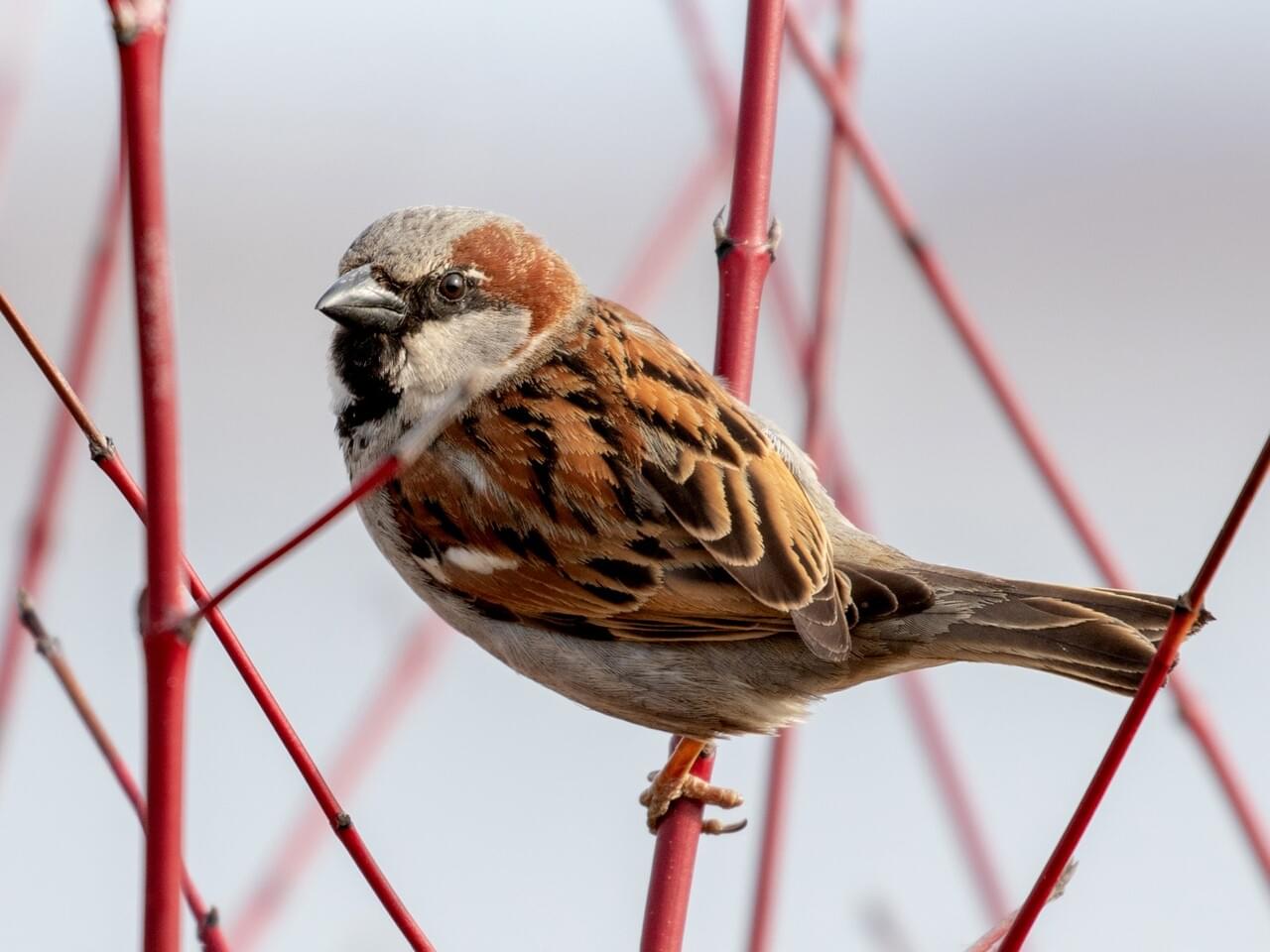
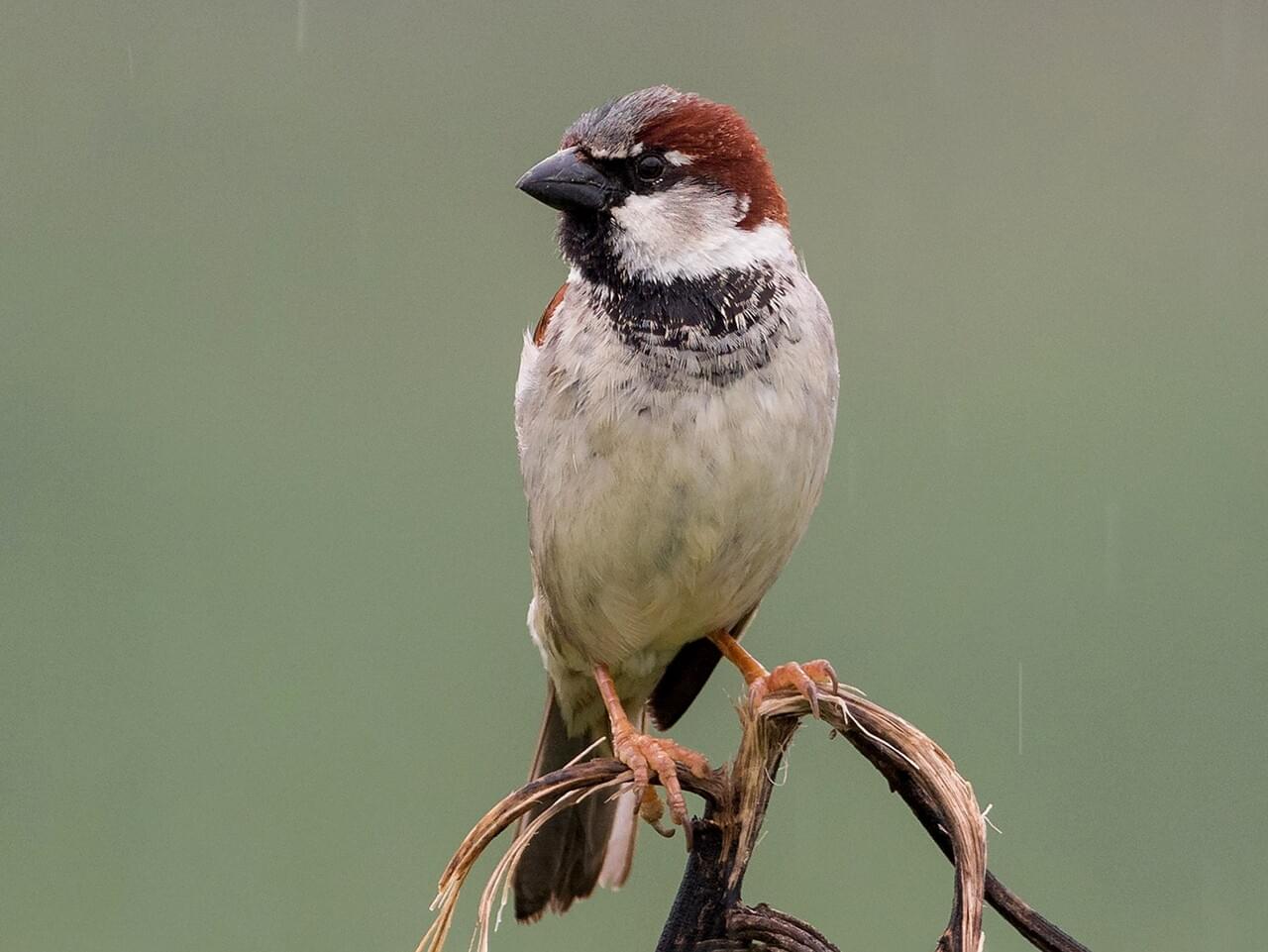
House Sparrows aren’t related to other North American sparrows, and they’re differently shaped. House Sparrows are chunkier, fuller in the chest, with a larger, rounded head, shorter tail, and stouter bill than most American sparrows.
Color Pattern
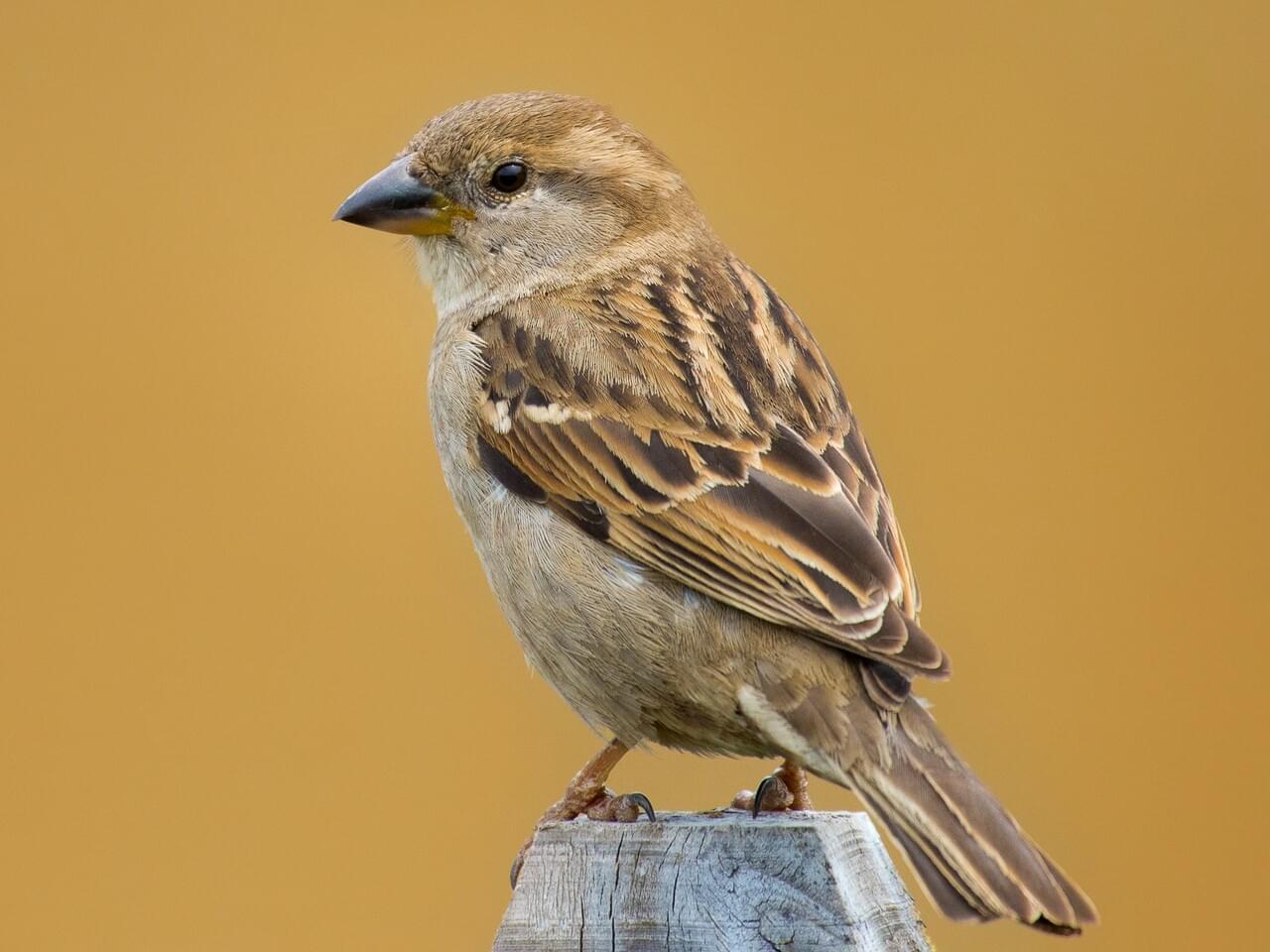
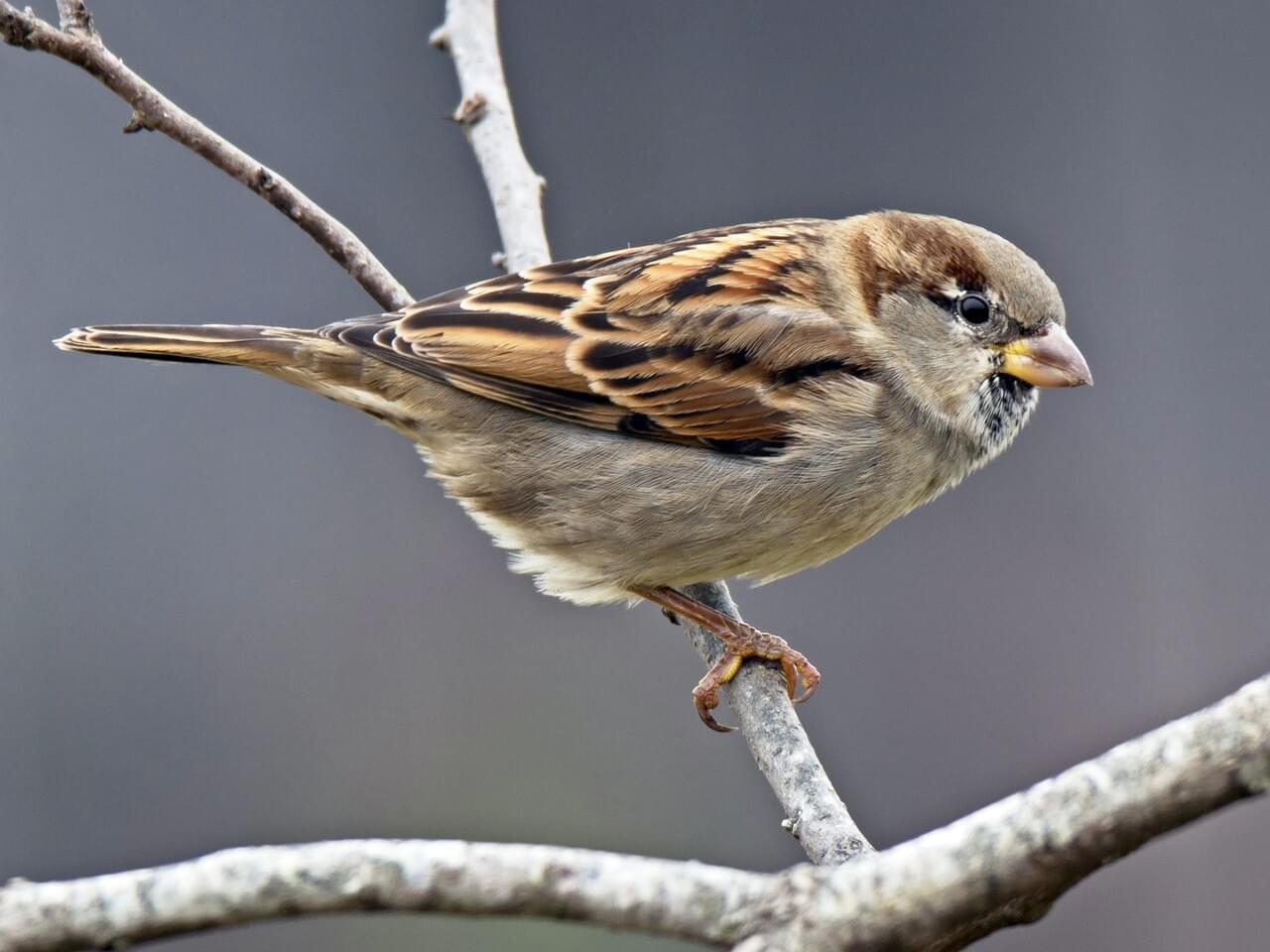
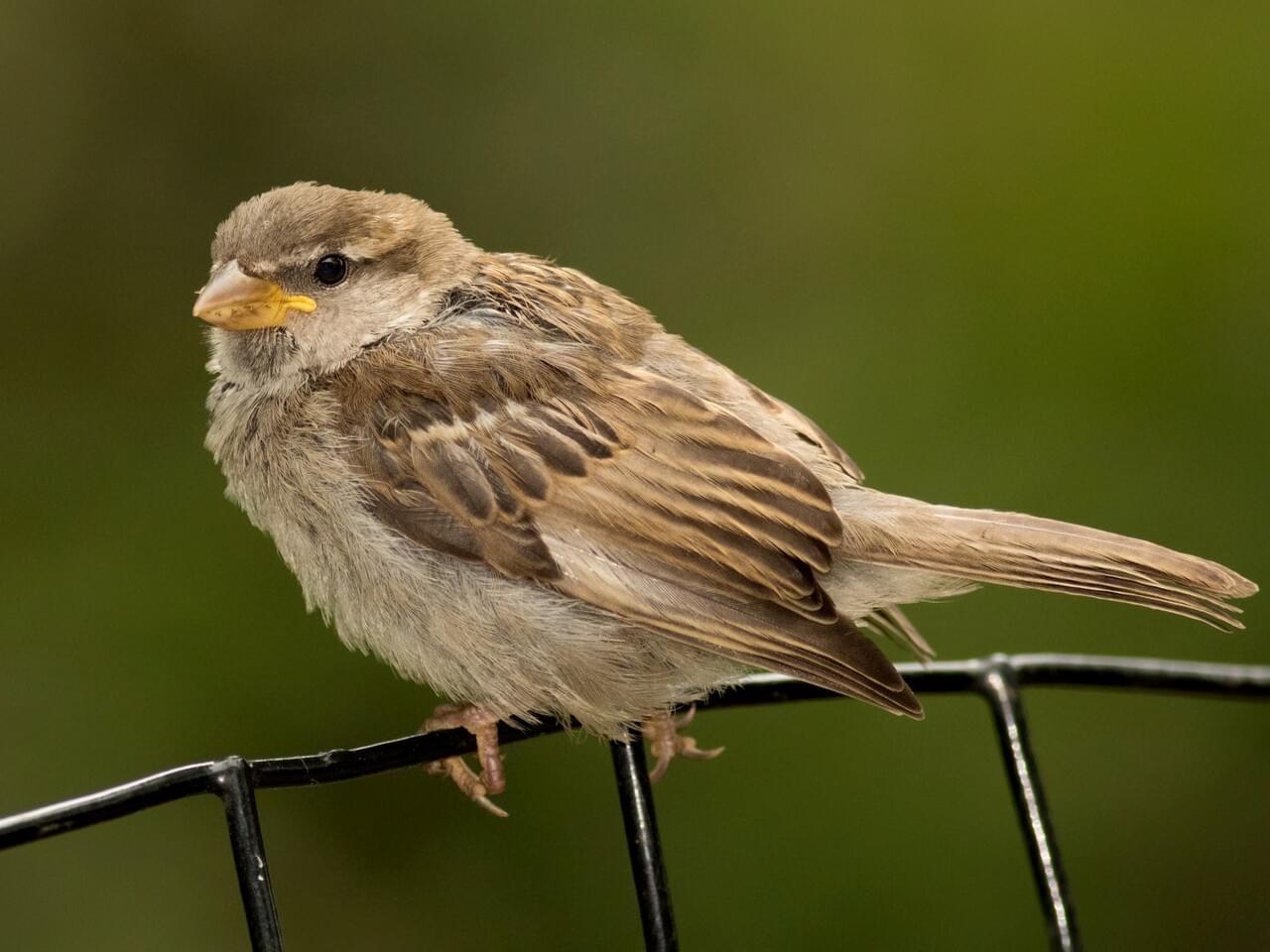
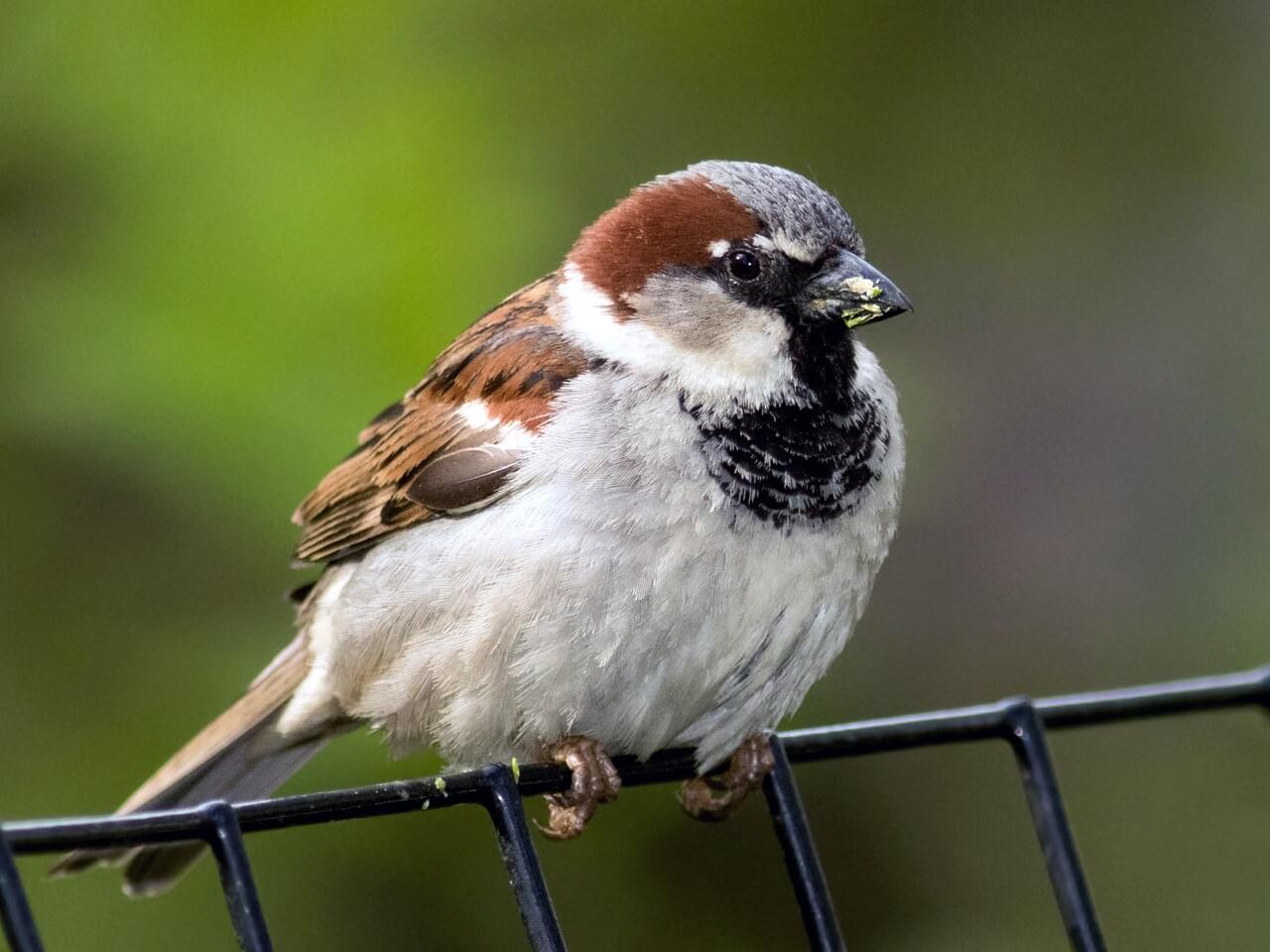
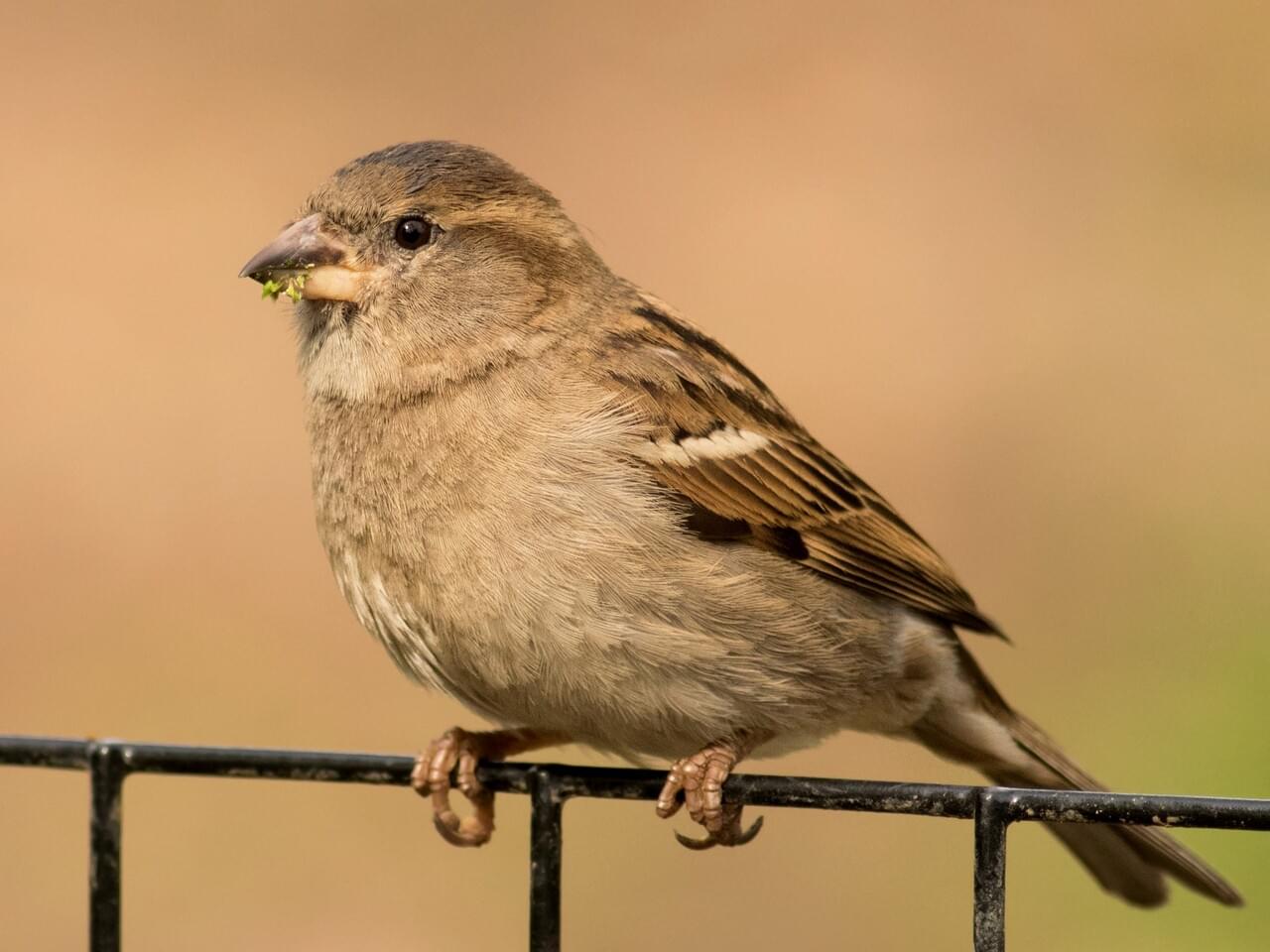
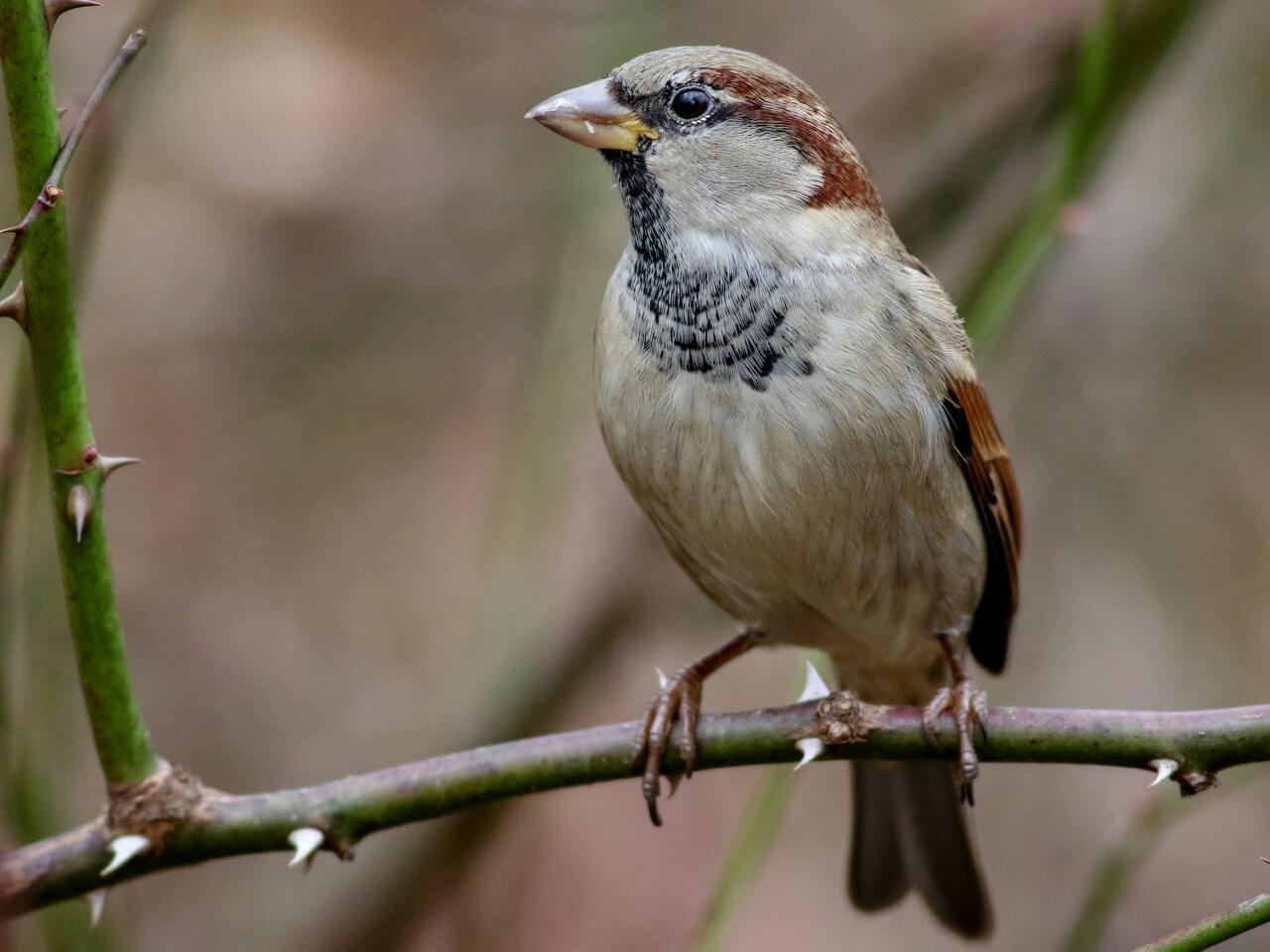
Male House Sparrows are brightly colored birds with gray heads, white cheeks, a black bib, and rufous neck – although in cities you may see some that are dull and grubby. Females are a plain buffy-brown overall with dingy gray-brown underparts. Their backs are noticeably striped with buff, black, and brown.
Plumage Photos
Similar Species
The female Dickcissel has a longer, heavier bill than a female House Sparrow, with a white chin, dark whisker stripe, and usually a tinge of yellow in the eyestripe and on the chest. Black-throated Sparrows of the dry western U.S. are all gray, white, and black on the head, with no rufous. Harris's Sparrows are plain brown on the face, without the male House Sparrow's white cheeks, and the forehead is black. Juvenile White-crowned Sparrows look like female House Sparrows but have reddish-brown crowns and thin white wingbars. Eurasian Tree Sparrows, which live around St. Louis, Missouri, have an entirely rufous crown and a dark spot on the cheek.
Did you know?!
- 100 House Sparrows were bought by Mr. Nicolas Pike for $200 from England and released in Brooklyn, NY, in the fall the 1851 and the spring 1852. By 1900 House Sparrows had spread throughout most of America.
- House Sparrows can swim if they are forced to! An adult swam to shore when escaping a hawk. Nestlings that have fallen into the water from their nests can also swim to land.